Only in Mage Pro.Try our fully managed solution to access this advanced feature.
Overview
Mage Pro workspaces provide isolated environments for developing and managing data pipelines. Each workspace operates as a separate container instance, allowing for independent resource allocation and configuration management.Core Components
- Runtime Environment: Containerized Python environment
- Storage System: Persistent volume for code and data
- Resource Manager: Kubernetes-based resource allocation
- Access Control: Role-based permission system
To utilize the collaborative workspace environment, please contact Mage to request an account upgrade.
The Mage team will need to enable this feature for your organization.
Setup Guide
- Step 1: After logging into the Mage Pro environment you will be in the Workspaces interface (url: https://cluster.mage.ai/[cluster-uuid]/manage). Press the Create new workspace button.
- Step 2: Give the workspace a name.
- Step 3: Click the dropdown arrow and toggle on the Kubernetes configuration if you need to custom configure your Kubernetes container. (see Kubernetes container configuration section for more details).
- Step 4: Click the Lifecycle (optional) dropdown to create lifecycle management policies (see Lifecycle management policies section for more information).
- Step 5: Click the create button and wait a few minutes for your workspace to start.
- Step 6: Once your workspace is running, click the workspace open button under the open column in the workspace management interface.
Workspace Configuration Options
Mage Pro workspaces support comprehensive configuration options that allow you to customize your workspace environment, resources, and behavior. Configuration options vary by cluster type (Kubernetes, Docker).Basic Workspace Configuration
All workspace types support these basic fields:name(required): The workspace name. Must be unique within your cluster.lifecycle_config(optional): Lifecycle management policies (see Lifecycle Management Policies section below).
Kubernetes Workspace Configuration
Kubernetes workspaces support the following configuration options:Container Configuration (YAML)
Thecontainer_config field accepts a YAML string that allows you to configure:
- Resource Configuration: Controls memory and CPU allocation for your workspace container
- Environment Variables: Customize environment variables for your workspace
- Other Container Settings: Any other Kubernetes container configuration options
Environment configuration
Setting USER_CODE_PATH
If you’ve modified the default USER_CODE_PATH environment variable in the base project (Mage Pro management portal), update your Kubernetes configuration:
Adding Other Environment Variables
You can define additional environment variables in the same env section to further configure your workspace:WORKSPACE_ENV_PATTERN at the cluster level, the ENV variable will be automatically set based on the workspace name. You can still explicitly set ENV in the container configuration to override the pattern. See the Auto-set ENV variable from workspace name section for more details.
Resource configuration (optional)
Optionally configure your workspace’s computing resources in Kubernetes:Complete Kubernetes Container Configuration Example
Here’s a complete example of a Kubernetescontainer_config YAML:
requests: Minimum resources guaranteed to your workspace. Kubernetes will ensure these resources are available.limits: Maximum resources your workspace can use. Prevents resource overconsumption and ensures fair resource allocation across workspaces.
container_config YAML, including:
- Environment variables (
env) - Resource requests and limits (
resources) - Volume mounts (
volumeMounts) - Security context (
securityContext) - And other Kubernetes container spec fields
Pod Scheduling Configuration
You can control which nodes your workspace pods are scheduled on usingnodeSelector, affinity, and tolerations.
Node Selector
UsenodeSelector to schedule workspace pods on nodes with specific labels. This is the simplest way to target specific nodes.
Example:
Affinity
Useaffinity for more advanced scheduling rules, including node affinity, pod affinity, and pod anti-affinity.
Node Affinity Example:
Tolerations
Usetolerations to allow workspace pods to be scheduled on nodes with taints.
Example:
Complete Example with Scheduling Configuration
Here’s a complete example combining resource configuration with pod scheduling:nodeSelector, affinity, tolerations) are applied to the workspace pod, not the container. They control where Kubernetes schedules your workspace pods in the cluster.
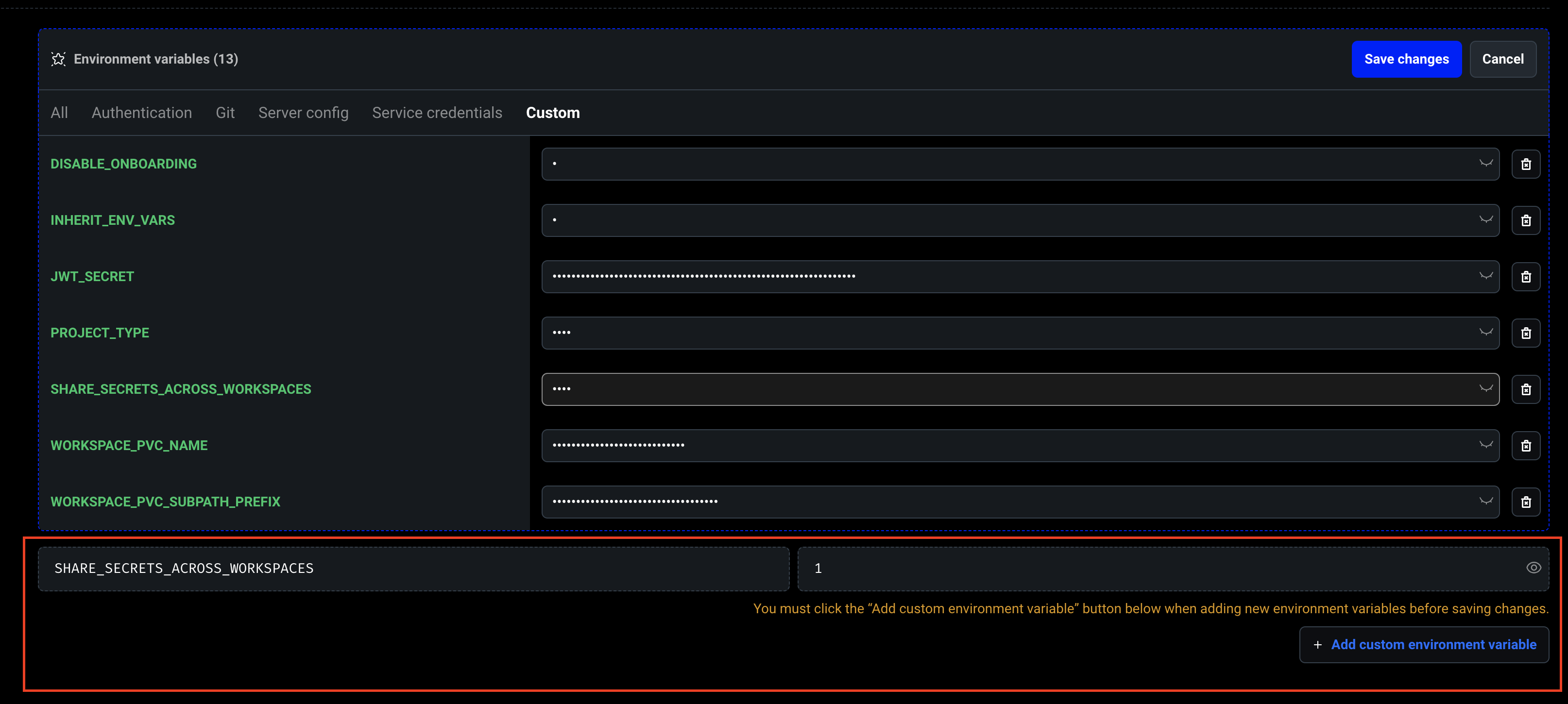
Share secrets across workspaces
To share secrets across different workspaces, you need to set theSHARE_SECRETS_ACROSS_WORKSPACES environment variable at the cluster level (not at the workspace level) and set the value to 1 to enable this feature. This will allow developers to share their secrets across different workspaces within a cluster.
Note: The SHARE_SECRETS_ACROSS_WORKSPACES environment variable must be set on the main cluster container, not on individual workspaces.
Inherit environment variables
Configuring your Mage Pro workspaces to inherit the main cluster’s environment variables is essential for efficiently configuring your workspace container. The following options allow you to control how variables are shared within your environment. To enable environment variable inheritance in workspaces, you must set theINHERIT_ENV_VARS environment variable at the cluster level (not at the workspace level):
INHERIT_ENV_VARS environment variable must be set on the main cluster container, not on individual workspaces. This applies to both Managed Cloud and Self-hosted Mage Pro.
Managed Cloud
TheUSER_DEFINED_VARS environment variable (set at the cluster level) lets you control which environment variables are inherited by workspaces.
It accepts a comma-separated list of variable names, giving you flexibility to include only the configuration values you need across workspaces.
- If
USER_DEFINED_VARSis not set: all environment variables will be inherited automatically. - If
USER_DEFINED_VARSis set: only the specified variables will be inherited.
DEV_ENV_*).
Self-hosted Mage Pro (Hybrid Cloud, Private Cloud, On-prem)
You must setUSER_DEFINED_VARS at the cluster level to define which variables to inherit:
Auto-set ENV variable from workspace name
You can automatically set theENV environment variable for each workspace based on its name using the WORKSPACE_ENV_PATTERN cluster-level environment variable. This eliminates the need to manually set ENV in each workspace’s container configuration.
Configuration:
Set WORKSPACE_ENV_PATTERN at the cluster level (not at the workspace level):
{workspace_name}: Placeholder that will be replaced with the actual workspace name- The pattern supports any string with the
{workspace_name}placeholder
- If
ENVis not explicitly set in a workspace’s container configuration, it will be automatically set using the pattern - If
ENVis explicitly set in the workspace’s container configuration, that value takes precedence over the pattern - The pattern is only applied when
WORKSPACE_ENV_PATTERNis defined
my-workspace, this sets ENV=dev_my-workspace.
Example 2: Environment prefix with suffix
analytics, this sets ENV=env-analytics-prod.
Example 3: Just workspace name
production, this sets ENV=production.
Integration with environment-specific variable inheritance:
When ENV is automatically set via WORKSPACE_ENV_PATTERN, it enables the environment-specific variable inheritance feature. You can then use:
ENV=dev_my-workspace for a workspace named my-workspace, and that workspace will inherit all variables matching DEV_ENV_* from the cluster.
Inherit variables by workspace environment
You can define inheritance rules per workspace environment using cluster-level environment variables with theENV variable:
{env_value}: value of theENVvariable in the workspace.{pattern}: wildcard/regex pattern for matching variables.
ENV=dev inherits all variables matching DEV_ENV_*.
Combined example with WORKSPACE_ENV_PATTERN:
- A workspace named
workspace1automatically getsENV=dev_workspace1and inherits variables matchingDEV_ENV_* - A workspace named
workspace2automatically getsENV=dev_workspace2and inherits variables matchingPROD_ENV_*
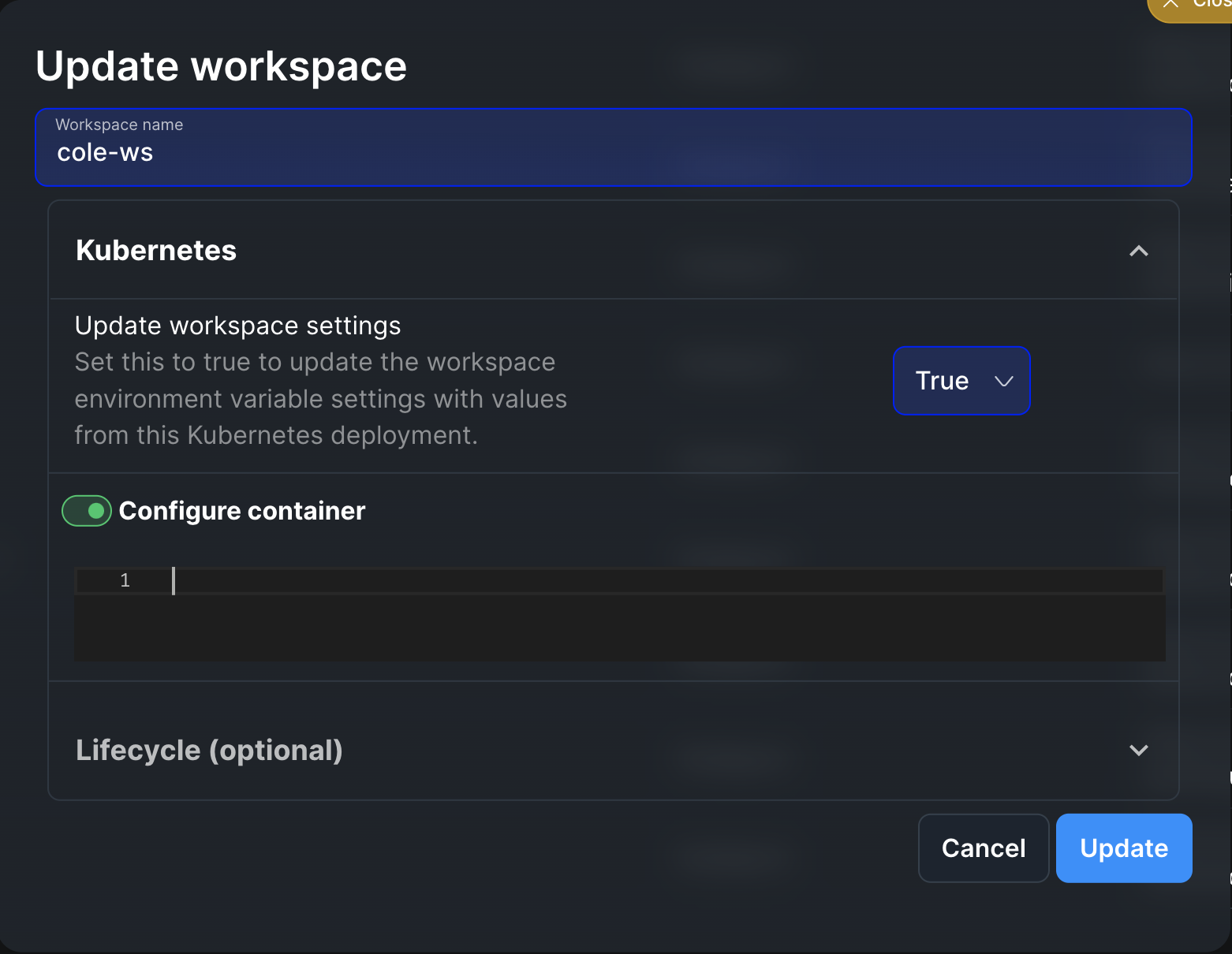
Updating workspaces after environment variable changes
When you add or modify environment variables in your base cluster, existing workspaces will not automatically inherit these changes. To ensure your workspaces reflect the updated environment configuration, you must restart the affected workspaces. To update a workspace:- Open the workspace settings by clicking into the workspace you want to update
- Click the update button for your workspace

- Click the dropdown arrow on the Kubernetes configuration section
- Toggle the “update workspace settings” option to true
- Click update
Lifecycle Management Policies (Optional)
Mage Pro workspaces support various lifecycle management policies that control how your workspace behaves throughout its runtime. These policies include automated termination settings, pre-initialization scripts, and post-initialization procedures, giving you complete control over your workspace’s behavior from startup to shutdown. Lifecycle configuration is specified in thelifecycle_config field as a YAML object:
Termination Policy
The termination policy controls how your workspace shuts down when inactive. Configuration:enable_auto_termination(boolean): Enable or disable automatic termination. Defaults tofalse.max_idle_seconds(integer): The number of seconds of inactivity before the workspace is automatically terminated. The idle time is measured in seconds, and you can set this duration based on your needs. For example:1800seconds = 30 minutes3600seconds = 1 hour7200seconds = 2 hours
Pre-Start Scripts
Pre-start scripts run before your workspace container is initialized. These scripts must include aget_custom_configs method that returns a dictionary of configurations. This is where you can set up environment variables, modify container configurations, and prepare any necessary resources. The script executes before any workspace services start, making it ideal for initial setup and configuration tasks.
Configuration:
pre_start_script_path(string): Path to the pre-start script. Can be:- Absolute path:
/absolute/path/to/script.sh - Relative path:
scripts/pre_start.sh(relative to the root project directory)
- Absolute path:
Post-Start Scripts
Post-start scripts execute after your workspace is fully initialized and running. You can specify either a direct command or provide a path to a script for more complex procedures. These scripts are typically used for starting services, performing health checks, or completing any additional setup tasks that require the workspace to be fully operational. Configuration:post_start.command(array of strings): Direct command to execute. Example:["echo", "Workspace started"]post_start.hook_path(string): Path to a script file. Can be:- Absolute path:
/absolute/path/to/hook.sh - Relative path:
scripts/post_start.sh(relative to the root project directory)
- Absolute path:
command or hook_path, or both. If both are specified, the command will execute first, followed by the hook script.
Example 1: Single post-start command
post_start.sh contains multiple commands:
Setting workspaces for self-hosted Mage Pro cluster
This section applies to self-hosted Mage Pro clusters only. These configurations are not applicable to Managed Cloud deployments.
Workspace Configuration Environment Variables
These environment variables are set at the cluster level to configure default workspace behavior. They control how workspaces are created, what storage they use, and how they’re exposed via ingress.Ingress Configuration
-
WORKSPACE_INGRESS_NAME(optional): Name of the Kubernetes ingress resource to use for workspaces. Defaults to the cluster UUID (MAGE_CLUSTER_UUID). If not set, workspaces will be accessible through the service directly rather than via ingress. -
WORKSPACE_INGRESS_TYPE(optional): Type of ingress controller to use. Supported values:nginx(default): Use NGINX ingress controlleralb: Use AWS Application Load Balancer ingressistio: Use Istio ingress gateway
nginx -
WORKSPACE_INGRESS_PATH_TYPE(optional): Path type for ingress paths. Supported values:ImplementationSpecific(default): Path matching is implementation-specificPrefix: Path must match as a prefix
ImplementationSpecific
Storage Configuration
You can configure workspace storage in one of two ways:Option 1: Individual PVCs per Workspace (using WORKSPACE_STORAGE_CLASS)
-
WORKSPACE_STORAGE_CLASS(optional): Kubernetes storage class name to use for workspace persistent volumes. When configured, each workspace will create its own PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) using this storage class. Default:efs-sc-us-west-2Use case: When you want each workspace to have its own isolated storage volume.
Option 2: Shared PVC across Workspaces (using WORKSPACE_PVC_NAME + WORKSPACE_PVC_SUBPATH_PREFIX)
-
WORKSPACE_PVC_NAME(optional): Name of an existing PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) to share across all workspaces. When set, all workspaces will use this shared PVC instead of creating individual PVCs. -
WORKSPACE_PVC_SUBPATH_PREFIX(optional): Prefix for subpaths when using a shared PVC. Each workspace will use a separate subfolder under this prefix to isolate its data. Required whenWORKSPACE_PVC_NAMEis set. Example: IfWORKSPACE_PVC_SUBPATH_PREFIX=workspaces, a workspace namedmy-workspacewill use the subpathworkspaces/my-workspace. Use case: When you want to share storage across multiple workspaces and manage storage more efficiently.
WORKSPACE_STORAGE_CLASS (for individual PVCs) or WORKSPACE_PVC_NAME + WORKSPACE_PVC_SUBPATH_PREFIX (for shared PVC), but not both. If both are configured, the shared PVC option takes precedence.
Pod Configuration
-
INHERIT_POD_ANNOTATIONS(optional, boolean): Iftrue, workspace pods will inherit annotations from the main cluster pod. This is useful for passing through annotations like Prometheus scraping labels, service mesh configuration, etc. Default:false
Example Configuration
Example 1: Individual PVCs per workspaceDocker Workspace Configuration
Docker workspaces support additional configuration options specific to Docker containers:Docker Workspace Environment Variables
These environment variables are set at the cluster level to configure default Docker workspace behavior:DOCKER_HOST(optional): Docker daemon host. Defaults tounix://var/run/docker.sock.DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY(optional): Enable TLS verification for Docker connection. Set to1to enable,0to disable. Defaults to0.DOCKER_CERT_PATH(optional): Path to TLS certificates for Docker connection.DOCKER_SWARM_MODE(optional): Enable or disable Docker Swarm mode. Set to1to enable,0to disable. Defaults to0.
Docker Container Configuration (YAML)
Similar to Kubernetes, Docker workspaces support acontainer_config YAML string:
Example Docker Workspace Configuration:
container_config field is the primary way to configure image, volumes, and environment. The system will parse this YAML string and extract:
image: Docker image to usevolumes: Volume mounts configurationenvironment: Environment variablespublic_url: Public URL for the workspace
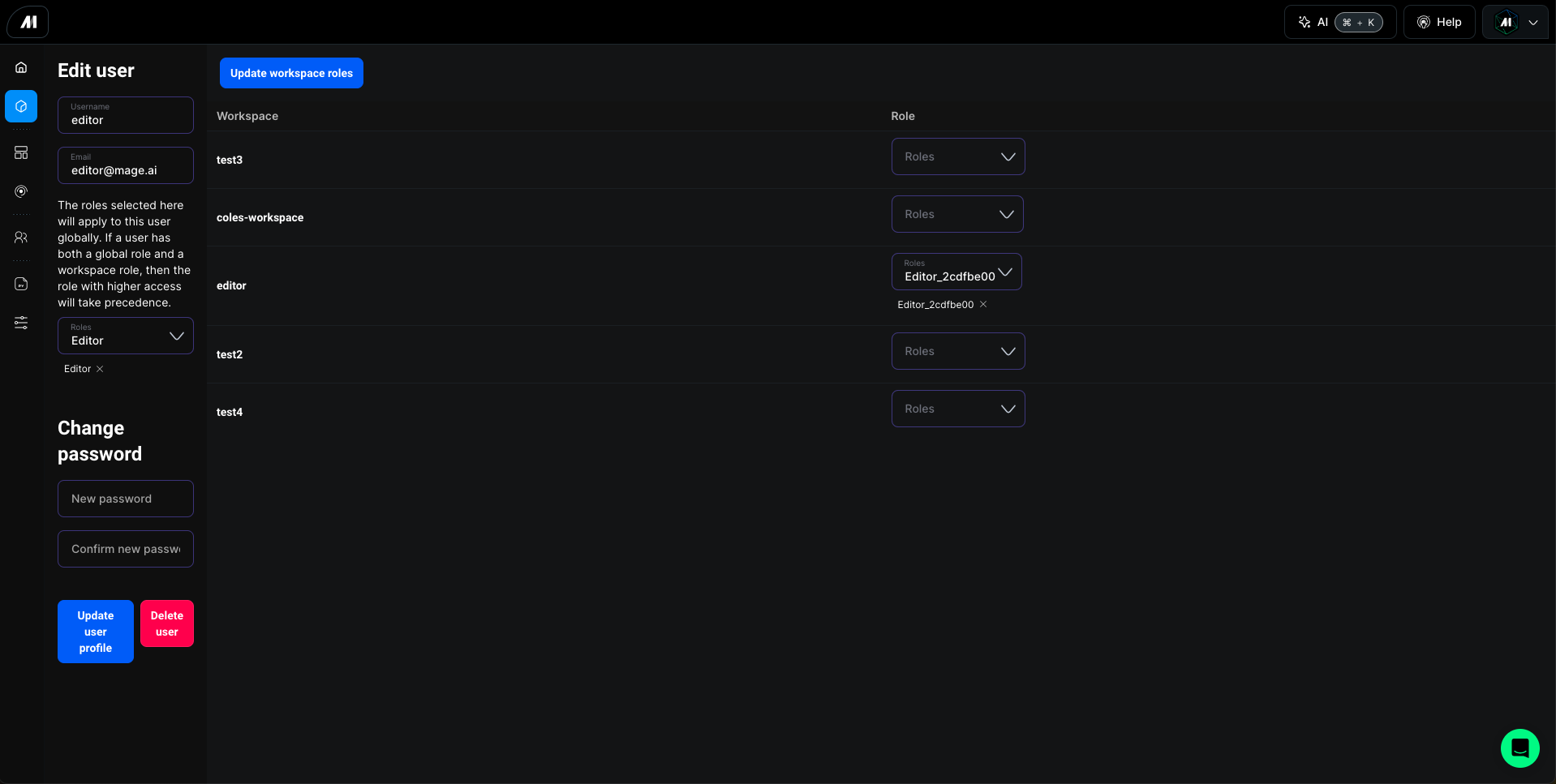
Global Roles
Users can be assigned global roles that apply across all workspaces within your Mage Pro environment. Global role assignment is managed by project administrators through Users tab in left navigation menu located in the main project interface.Workspace-Specific Roles
Individual workspaces can have unique role settings. Workspace owners can:- Assign user roles specific to their workspace
- Modify existing role assignments
- Remove user access to their workspace