
Overview
Mage supports user authentication to secure access to the UI and APIs.
Authentication is required before creating, managing, or running pipelines.
-
Mage OSS:
- Versions 0.9.78 and above → user authentication is enabled by default.
- Versions 0.8.4 – 0.9.77 → user authentication can be turned on optionally.
-
Mage Pro:
- User authentication is always enabled by default.
For Mage OSS versions 0.8.4 – 0.9.77, you can enable authentication manually by setting the following environment variable:
| |
|---|
| Name | REQUIRE_USER_AUTHENTICATION |
| Value | 1 |
Set access token expiration time
You can set the MAGE_ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRY_TIME environment variable to customize the expiration time
of a Mage access token. The value should be the length of time in seconds.
Defaults to 2592000 which is 30 days.
| |
|---|
| Name | MAGE_ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRY_TIME |
| Value | 2592000 |
Running Mage in Docker
If you’re running Mage using Docker, you can run Mage and set the environment variable
in the docker run command. Follow these instructions
to learn how.
Set the environment variable using -e REQUIRE_USER_AUTHENTICATION=1.
For example:
docker run -it -p 6789:6789 \
-v $(pwd):/home/src \
-e REQUIRE_USER_AUTHENTICATION=1 \
mageai/mageai /app/run_app.sh mage start demo_project
Running Mage without Docker
If you installed Mage using pip, conda, poetry, etc. and are running it using the mage start
command, then you need to set the environment variable on your workstation.
macOS
Run the following command to set environment variables:
export REQUIRE_USER_AUTHENTICATION=1
Windows
Read Microsoft’s instructions
on how to do this.
Default owner user
When Mage starts, if there is no existing owner user, then a new user will be created with owner
permissions (e.g. all permissions).
The owner user can create, edit, and delete other users.
Here are the default credentials for the owner user to sign in with:
| Field | Value |
|---|
| Email | admin@admin.com |
| Password | admin |
Available in versions >= 0.9.72
DEFAULT_OWNER_EMAILDEFAULT_OWNER_PASSWORDDEFAULT_OWNER_USERNAME
Sign in page
Before using Mage, users will have to sign in at /sign-in. If you go to a page that requires
authentication and you’re not signed in, you’ll be redirected to the sign in page.
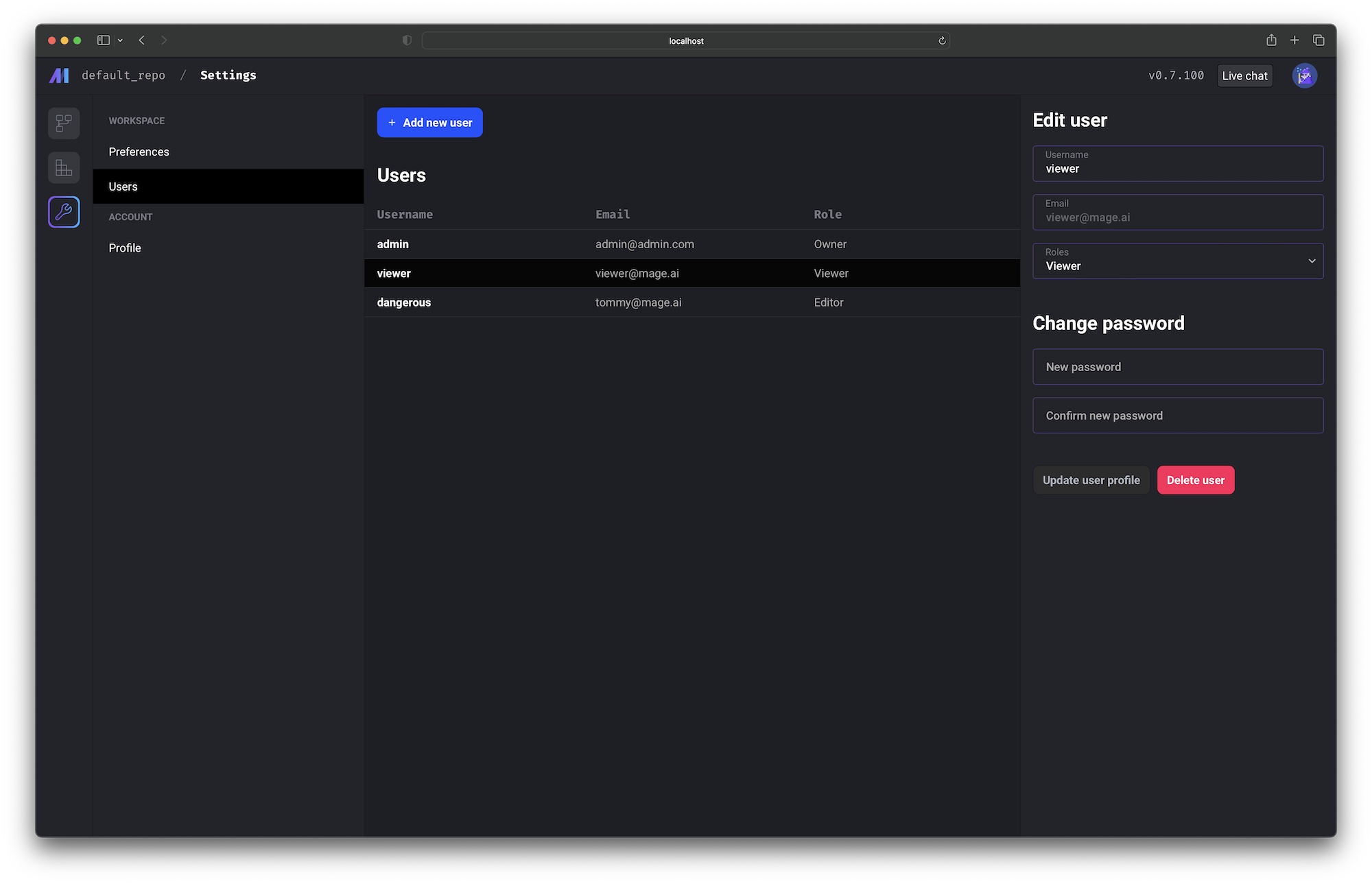
User management page
If you’re signed in as the owner user, you’ll have access to the user management page at
/settings/workspace/users.
On this page, you can:
- Add new users
- Edit existing users
- Reset user passwords
- Delete users
Roles and permissions
| Role | Permissions |
|---|
| Viewer | Can read. |
| Editor | Can do everything a viewer can, create, update, and delete. |
| Admin | Can do everything a viewer can, an editor can, and manage users who are viewers/editors (update usernames, emails, passwords, and make viewers editors or vice versa. |
| Owner | In addition to what admins can do, add and delete users. Manage all users, including admins/owners. Make other users any role, including admins/owners. |
Authenticated requests
If you require user authentication by turning it on via the environment variable mentioned above,
then each API request the front-end client makes to the backend server will include an API key
and an OAuth2 token.
The API key and OAuth2 token is used to authenticate the incoming request. If the requester
doesn’t have the proper permissions, the backend server will respond with a 4XX error code.
API errors
If a page loads and no data is visible, it could either mean there is no data or the user
doesn’t have the proper permissions.
If there is no visible error message on the page, you can view the browser’s network tab and
inspect the API request response to view the full error details
(we’re working on showing better errors and making it easier to display them).
Learn how to view the network requests in Chrome by following these
instructions. | Error code | Description |
|---|
401 | Expired OAuth token. |
401 | Invalid OAuth token. |
402 | Record is invalid. |
403 | Invalid API key. |
403 | Unauthorized access. |
404 | Record not found. |
500 | API resource error. |


